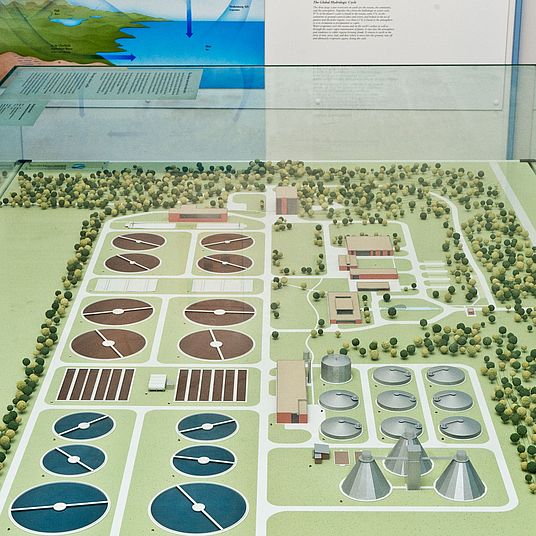
![[Translate to English:] Das System Erde dargestellt durch verschiedene Globen.](https://www.deutsches-museum.de/assets/_processed_/a/8/csm_Ausstellung_Umwelt_CD_L_7596_354_c741affa40.jpg)
Photo: Deutsches Museum | Christian Illing
Man and Environment
Environment – Man and Technology on Planet Earth
How do we pollute our environment? Why do we pollute it more than we used to? What can we do to change this? Find out more in the Environment exhibition!
Human Activities and their Consequences
Ever since humans have walked the Earth, they have interfered with their environment – through arable and livestock farming, deforestation and the construction of settlements, traffic routes, power plants and industrial facilities. At the same time, the global population has grown and continues to grow. There has been a rise in prosperity, leading to the increased consumption of energy and raw materials and creating waste and pollutants in the process.
This exhibition presents various aspects of environment-related research, technology, cultural history and politics. It starts by examining the causes of environmental pollution, before guiding you through the history of environmental awareness. It addresses water, waste and recycling, the effects of air pollution, and climate change. Finally, it tries to identify technical and social solutions.
7.77 billionThe world’s population in 2020
583.9 trillionGlobal energy consumption (in joules) in 2019
4.8 tonnesAverage CO2 emissions per capita in 2018
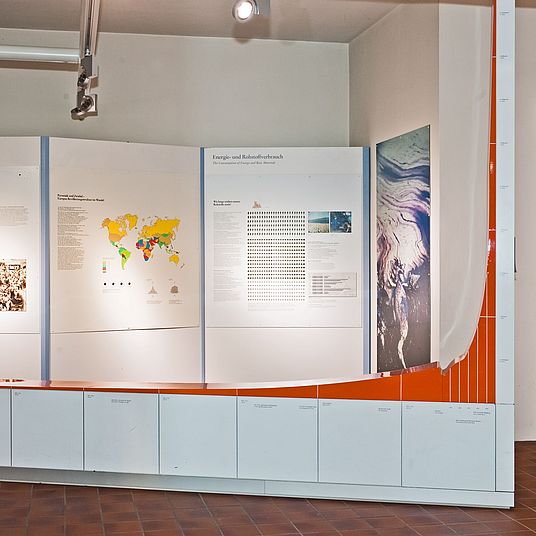
View inside the Environment exhibition. Photo: Deutsches Museum
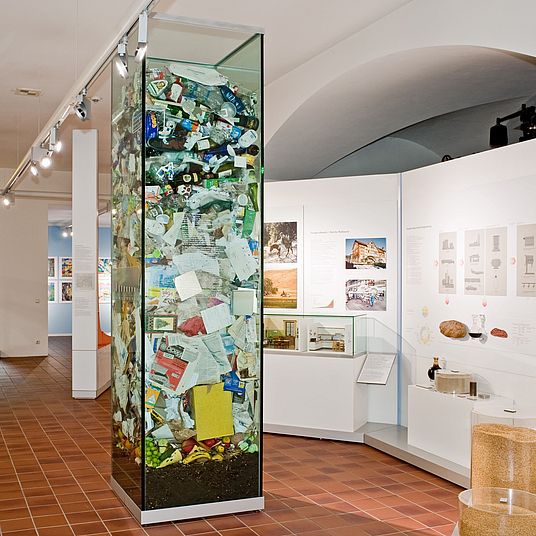
The column of waste in the exhibition. Photo: Deutsches Museum
Exhibition Themes
- History
The relationship between people and their environment varies in the different cultures around the world, and has changed over the course of history. - Growth
The growth in the world’s population, the increasing consumption of energy and raw materials, and the production of waste are all causes of environmental pollution. - Water
Clean drinking water is an increasingly scarce resource. At the same time, the amount of waste water is so high that it has to be purified at wastewater treatment plants. - Air
Air pollution has dropped in some parts of the world thanks to the use of technology – but this is by no means the case everywhere. - Climate
CO2 and other greenhouse gases caused by human activity are one of the major causes of global climate change. We must act now! - Fishing
Due to high levels of fishing in recent decades, the oceans’ fish stocks, which were once considered inexhaustible, are reaching their limits.
“"We’ll need a lot of luck and drastic action to stay below 1.5 degrees."”
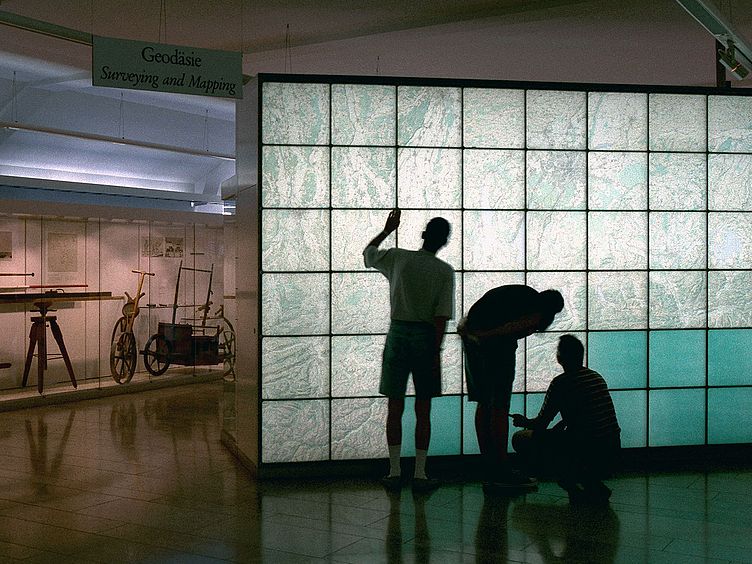
Inside the Environment Exhibition
Supporting Materials and Publications


Virtual Tour
Discover the exhibition in 360°: click the mouse or touch the screen to look around in any direction. The virtual tour also includes text, films and audio information for many of the exhibits.
Virtual Tour through the Environment Exhibition
Facts
- Exhibition area: around 300 sqm
Any Questions?
![]()
Dr. Sabine Gerber-Hirt
Leitung Hauptabteilung AI Naturwissenschaften / Leiterin Abt. wiss. Volontärinnen & Volontäre / Kuratorische Leiterin Ausstellung Landwirtschaft & Ernährung / Kuratorin für Umwelt & Deutscher Zukunftspreis / Leitung Ausstellungsbeirat des Deutschen Museum
Deutsches Museum
80306 MünchenTelephone +49 89 2179 565
Fax +49 89 2179 99350
Email s.gerber-hirt@deutsches-museum.de
Do you have organizational questions?
Cornelia Schubert
Assistance to department heads, main department heads and curators
Susanne Schmölz
Assistance to department heads, main department heads and curators